As healthcare needs grow across India, particularly in smaller towns, the demand for well-planned hospitals and nursing homes is increasing. But designing a hospital is not like building a house or a showroom. It requires a deep understanding of space zoning, movement flow, compliance standards, and long-term growth needs.
If you’re planning to build a hospital or medical facility in Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal or in any other state across India, and wondering where to start, then we have got you covered. Today in this guide will walk you through the key steps of hospital building planning from an architectural perspective.
So are you ready? Let’s dive in.
Understanding Hospital Building Types
Before starting your design, it’s important to define the type and scale of the hospital you are planning to build. This helps determine the layout, zoning, services, and required floor space.
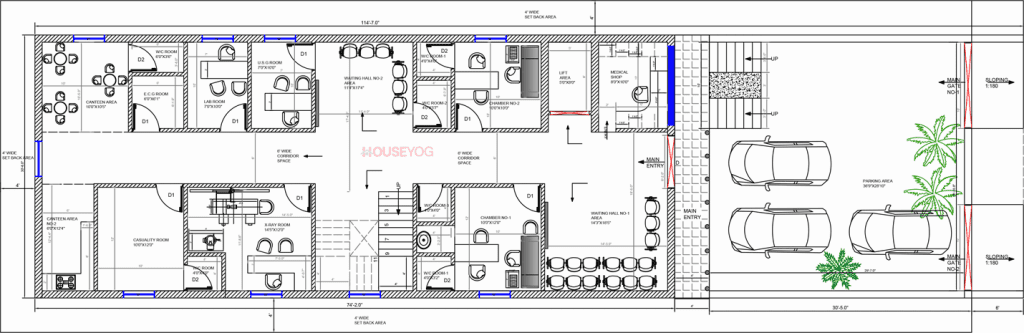

Common types of hospital setups in small towns:
- Clinic + Diagnostics Unit (500–1000 sq. ft.)
- 10 – 30 Bed Nursing Homes (G+1 or G+2 buildings)
- 50 – 100 Bed Multi-Specialty Hospitals
- Maternity Homes and Trauma Centres
Each of these setups comes with unique space requirements.
For example, a 30-bed nursing home needs proper ward planning, oxygen pipeline zones, and separate OPD and IPD movement.
Step-by-Step Hospital Planning Process
Designing a hospital is both a technical and functional task. Here’s how to approach it smartly in 2025:

Plot Size & Zoning
Make sure the land is permitted for institutional or commercial use. Leave space for:
- Emergency access roads
- Ambulance turning radius
- Parking zones
Zoning the Spaces
Divide the plot/floor plan into key zones:
- Public zones: Reception, Waiting area
- Clinical zones: OPD, ICU, Wards
- Support zones: Pharmacy, Lab, Admin office
Use zoning to reduce infection risk, improve navigation, and maintain privacy.
Entry/Exit Flow Planning
Separate the entry for patients, emergency vehicles, and staff. This helps avoid congestion and confusion during rush hours or in emergencies.
Vertical Circulation
For G+ buildings, proper lift, staircase, and ramp planning is essential, especially in hospital facilities. Minimum 6 – 8 ft staircases, ramps with handrails, and patient trolley lifts are a must.
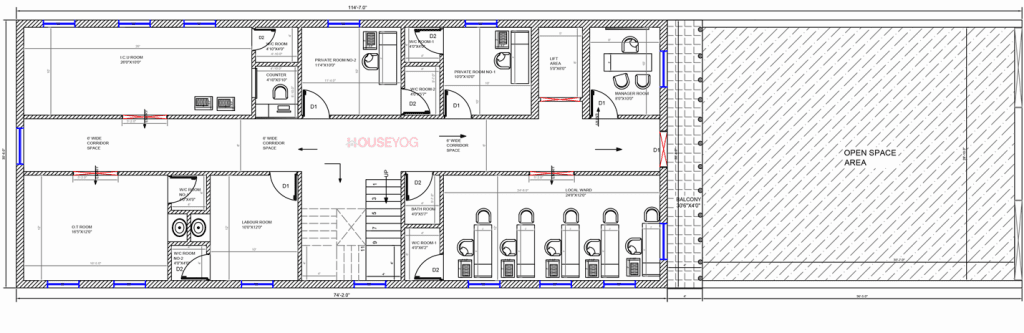
Key Functional Zones to Include
While the actual floor layout for a hospital building varies depending on the bed capacity and type of hospital, here are some zones every medical building should include:
| Zone | Purpose |
| Reception & Waiting | First contact area for patients |
| OPD Rooms | General and speciality consultation |
| Wards/ICU | For admitted patients |
| Diagnostics | X-ray, Pathology, Sonography etc. |
| Pharmacy | Attached or independent access |
| Toilets | Separate for male, female, and staff |
| Doctors’ Lounge | Rest & consultation space |
| Lift / Ramp | Movement for stretchers/patients |
| Kitchen/Canteen | For large hospitals |
Hospital Design Standards in India
There are specific national building codes and health standards for hospital buildings in India. While your architect will handle the technical drawings, it’s good to be aware of the standard guidelines:


Room Size & Space Norms
- OPD Room: 100–120 sq. ft. min
- Wards: 80–100 sq. ft. per bed (min spacing 3–4 ft between beds)
- ICU: 150–200 sq. ft. per bed
- Corridor: 6 ft minimum width for patient mobility
Safety & Sanitation
- Fire exits and extinguishers on each floor
- Generator and UPS rooms
- Drainage, water supply, and oxygen pipelines
For detailed norms, refer to IS 12433 and NBC (National Building Code) health facilities chapter
Design Tips for Comfort and Efficiency
Patient care goes beyond equipment – the hospital building itself plays a major role in comfort and healing.
Here are some design practices recommended by experts:
- Natural ventilation and lighting
- Ceiling height of 10–12 ft
- Non-slippery flooring and anti-bacterial paint
- Sound insulation in consultation rooms
- Separate entry for OPD and Emergency
- Green buffer zones or small courtyards for recovery areas
Vastu Considerations for Hospital Planning
While not mandatory, Vastu-compliant designs offer peace of mind for many owners and patients. Many Indian hospital owners still prefer to follow Vastu principles, especially in small towns.
Here are the important Vastu Tips for Hospitals worth knowing:
- Main entry from East or North
- Emergency Room in Southeast
- Pharmacy in North-East
- Wards facing East for sunlight
- ICU in South-West (peaceful zone)
Common Mistakes to Avoid (Especially in Smaller Towns)
A poorly planned hospital is hard to operate and harder to scale. Avoid these mistakes:
- Single entry/exit leading to chaos
- No waiting area for relatives
- No provision for ramp/lift in G+ structures
- Mixing clean and contaminated zones
- Insufficient toilets or disabled-friendly access
- Parking planned AFTER building approval
A good architectural plan eliminates these errors early.
Cost Optimization and Materials
For budget-friendly hospital projects, especially in rural towns:
- Use modular designs (repeat OPD rooms, identical wards)
- Go for standard tile sizes and local brands
- Optimize for daylight and ventilation to cut electric load
- Use prefabricated partitions or PUF panels in selected zones
Design once, build smart, scale faster.
Planning for Lawn + Expansion Zones
If space allows, consider a landscape lawn or waiting garden near the entry. It improves aesthetics and serves as a peaceful area for relatives.
Also, don’t forget to plan space for future expansion:
- Leave a side margin to build extra wards
- Add provision for a lift if only stairs are being used for now
- Allocate a section for diagnostics, even if it’s not required initially
Why Hire a Professional Architect for Hospital Design?
Hospital buildings are complex. You’re dealing with patients, staff, emergencies, hygiene, and government approvals, all in one project. Having an expert by your side can make the process easier and future-proof.
A professional architect can help you with:
Site planning & zoning
Floor plan & bed layout
Structural & working drawings
Elevation & branding design
Sanction-ready drawings for approval
Cost-optimized, scalable building plans
Learn about our architectural design services and site planning services to know how we can help and add value to your hospital building project.
Download Hospital Planning Checklist. This checklist will be helpful for anyone planning to build a hospital or nursing home in India, especially in tier-2 or tier-3 towns.
Want a Custom Plan for Your Hospital Project?
Whether you’re building a 10-bed setup or a full nursing home, Houseyog offers custom architectural and structural planning services across India. Call/WhatsApp: +91 75960 58808 or contact us today!
FAQ: Hospital Design & Planning in India
For a 10–20 bed nursing home, at least 2000 to 3000 sq. ft. plot is needed, preferably a corner plot or a plot with a good and wide access road.
In most cities, commercial or institutional use permission is required. You can consult your local municipality/ Panchayat or a local architect to find out the local rules.
Ideally, 4 – 6 OPD rooms, a diagnostics unit, and at least one emergency ward will best suit your 30-bed hospital.
A. Yes. We offer sanction-ready drawings, structure, elevation, and working plans for hospitals and other types of residential and commercial buildings across India.






