Planning a school building in India requires far more than drawing classrooms and corridors. It demands a clear understanding of school building planning, school infrastructure requirements, safety norms, and modern educational needs. A thoughtfully designed school must be safe, functional, future-ready, efficient, and fully compliant with CBSE/State Board regulations.
Whether you’re constructing a new CBSE/ICSE school or upgrading an existing campus, the right approach to school architecture ensures long-term performance, smooth operations, and a high-quality learning environment. Your school building layout, zoning strategy, classroom sizes, and circulation patterns all play a direct role in shaping student comfort, safety, and academic outcomes.
As architects who have designed multiple CBSE schools, K–12 campuses, and institutional buildings across India, we’ve created this complete School Building Planning Guide to help you understand:
- School building design requirements
- Minimum land required for a school (CBSE norms)
- School zoning & campus master planning
- Classroom size standards and ideal dimensions
- Labs, library, admin block & sanitation planning
- Playground, circulation & safety norms
- School construction cost in India
- CBSE affiliation infrastructure norms
- MEP and ventilation requirements
This guide is designed to help school owners, trusts, NGOs, and educational planners make informed decisions and create a school campus that is compliant, cost-efficient, and truly student-centric.
What is School Building Planning?
School building planning is the process of designing the layout, infrastructure, safety systems, and facilities of a school so it meets CBSE or state board norms, supports effective learning, and remains functional and future-ready.
Now that you know what school building planning means, let’s explore the essential requirements that form the foundation of an efficient and compliant school campus.
School Building Planning Requirements (The Foundation)
Planning a school building requires far more than drawing classrooms and corridors. It begins with a clear understanding of the core school building requirements that shape the entire project. From deciding student capacity to meeting CBSE norms, every choice affects the school’s layout, safety, circulation, and long-term expansion potential.
In professional school architecture planning, these foundational decisions determine how efficiently the campus will operate, how comfortably students will learn, and how easily the school can scale in the future. Whether you’re designing a new school or expanding an existing one, defining these planning requirements early ensures that the school building is functional, compliant, cost-effective, and future-ready.
Below are the essential factors every school owner, architect, or educational trust must consider before starting the school layout plan:
Student Capacity & Growth Projection
School building design starts with estimating:
- Initial student intake (Year 1)
- Growth projection for 5–10 years
- Maximum class size (30/35/40 students)
- Number of sections per grade
A school should always be planned for future expansion, even if built in phases.
Type of School
Each school type requires a different architectural approach:
- Pre-primary
- Primary (1–5)
- Middle (6–8)
- Secondary/Senior Secondary (9–12)
- K–12 Integrated campuses
Ownership Model
Planning varies for:
- Trust/NGO schools
- Private unaided schools
- Corporate CSR schools
- Government-aided schools
Budget & Phasing Strategy
Most schools are built in phases, starting with:
- Classrooms
- Admin block
- Essential toilets
- Basic playground
Followed by labs, library, indoor sports, auditoriums, etc.
Teaching Philosophy
Modern schools may need:
- Smart classrooms
- Flexible furniture
- Activity zones
- Breakout spaces
- Open-learning corridors
Your educational model must drive your architecture — not the reverse.
Regulatory Compliance
Every school must follow CBSE affiliation infrastructure norms, NCERT/State board guidelines, municipal laws, fire safety rules (NBC India), and accessibility standards:
- CBSE affiliation building norms
- NCERT/State board guidelines
- Municipal building laws
- Fire safety (NBC India)
- Accessibility guidelines
Access, Traffic Flow & Surroundings
Safe entry and exit zones, drop-off lanes, bus circulation, and road width must be carefully planned.
These foundational decisions determine how efficiently the campus will operate and whether the school meets the school infrastructure requirements in India as prescribed by CBSE and State Boards.
Minimum Land / Plot Size Requirements to Build a School
Determining the minimum land required for a school is one of the most important steps in school building planning. The size, shape, and zoning potential of the plot directly influence classroom capacity, playground area, traffic movement, safety standards, and compliance with CBSE land requirement norms.
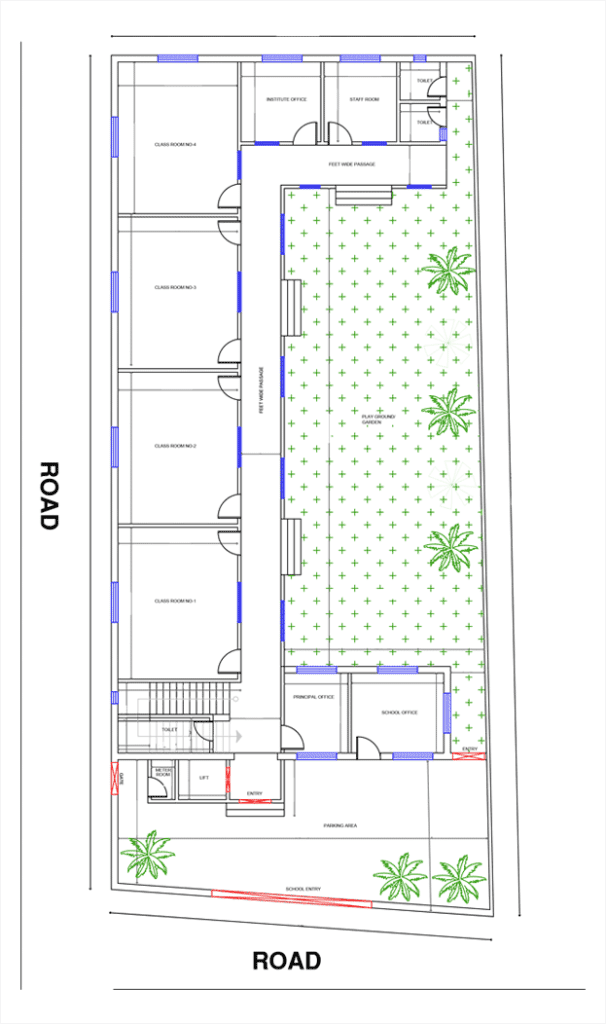

In India, school architecture must align with both national affiliation norms and local building regulations, making plot selection a critical foundation for the entire project. Whether you are planning a pre-primary school or a full K–12 campus, choosing the right plot ensures the school building design remains functional, scalable, and compliant for years to come.
Below are the essential land and plot size considerations every school owner and architect must evaluate before starting the school layout plan.
Minimum Land Required for a School (CBSE)
- Urban: 1 acre
- Rural: 1.5–2 acres
- Must include a suitable playground
(Reference: CBSE Affiliation Bye-Laws PDF)
Ideal Plot Size for Different School Types
| School Type | Recommended Plot Size |
| Pre-primary | 5,000–10,000 sq ft |
| Primary (1–5) | 10,000–25,000 sq ft |
| Middle School | 0.5–1 acre |
| Secondary | 1–1.5 acres |
| Senior Secondary | 1.5–2 acres |
| K–12 School | 2–5 acres |
Plot Shape, Frontage & Access
- Rectangular plots are most efficient
- Avoid L-shaped/irregular plots
- Road frontage: 40–60 ft minimum
- Approach road: 30–40 ft wide
Setbacks & Fire Tender Access
General norms:
- Front setback: 15–30 ft
- Side/rear setbacks: 10–20 ft
- Mandatory fire tender movement path
Playground Requirements
A usable playground area of 12,000–15,000 sq ft is recommended for sports and physical education.
School Zoning & Master Planning (Campus Layout Guide)
A successful school campus depends heavily on proper school zoning and master planning. This is where the overall layout of the school is defined — from academic blocks and admin areas to playgrounds, traffic movement, labs, and safety zones.
Proper zoning ensures that your school building layout plan supports smooth movement, safety, visibility, and future expansion.
In professional school building design, zoning ensures that each functional area—classrooms, labs, library, activity rooms, administration, and play zones—works smoothly without conflicts or congestion. Good school zoning not only improves student safety and comfort but also enhances operational efficiency and future expansion possibilities.
Effective school campus planning ensures that the entire layout is logical, accessible, compliant, and aligned with CBSE/State board requirements.
Below are the key zoning principles every school campus should follow before finalising the architectural layout.
Academic Zone
- Classrooms by block or grade
- Labs
- Library
- Activity rooms
Administrative Zone
- Reception
- Principal & VP office
- Accounts
- Meeting rooms
- Counselling rooms
Recreation & Play Zone
- Playground
- Outdoor sports courts
- Pre-primary play area
Service & Utility Zone
- Staff parking
- Bus parking
- Transformer & electrical room
- Water tanks & pump room
Circulation
- Clear pedestrian pathways
- Separate student/visitor/staff access
- Bus circulation loop
A proper zoning plan ensures smooth traffic flow, safety, and minimal operational disruption.
Classroom Planning (Size, Dimensions & Layout) for a Modern School
Proper classroom planning is the heart of school building design. The size, shape, and layout of each classroom directly influence student comfort, learning quality, ventilation, visibility, and safety. For schools in India, classroom design must align with CBSE classroom size requirements, national space standards, and modern teaching methodologies such as smart classrooms, activity-based learning, and flexible seating.
Understanding the right school classroom dimensions ensures that every room provides enough space for movement, optimal desk spacing, natural lighting, and efficient teacher supervision. Whether you’re designing classrooms for 30, 35, or 40 students, the goal is to create a learning environment that is both functional and future-ready.
Below are the recommended classroom size standards and school building design guidelines used in modern educational planning.
Area Per Student (CBSE/NCERT Norms)
Recommended 1.0–1.4 sq.m per student (≈ 10.5–15 sq.ft)
Classroom Area for 35–40 Students
| Students | Minimum Area | Ideal Area |
| 35 | 375–430 sq ft | 480–540 sq ft |
| 40 | 430–480 sq ft | 540–600 sq ft |
Ideal Classroom Dimensions
- 28 × 20 ft → 560 sq ft (Best for 35–40 students)
- 24 × 20 ft → 480 sq ft (Good for 30–35 students)
Classroom Shape
- Ideal: Rectangular (1:1.3 – 1:1.4 ratio)
- Avoid: Square rooms
Ventilation & Lighting
- 20–25% of the wall area should be windows
- 300–350 lux natural lighting
- Cross ventilation is essential
Furniture & Circulation
- Row spacing: 2–2.5 ft
- Teacher zone: 3 ft
- Side aisle: 3 ft for emergency circulation
If you need a deeper breakdown of room dimensions, layouts, and CBSE norms, you can also refer to our detailed guide on the Ideal Classroom Size for 35–40 Students. It explains recommended areas, layouts, ventilation standards, and space planning in detail.
Administrative Block Planning for a School in India
The administrative block serves as the operational backbone of any school campus. A well-planned school admin block design ensures smooth day-to-day management, efficient visitor handling, staff coordination, and secure access control. Since parents, teachers, and visitors interact with the admin block more than any other area, its layout must be functional, welcoming, and strategically located near the school’s main entrance.
Effective administrative block planning includes dedicated spaces for the principal, vice-principal, accounts, records, counselling, and staff rooms — all arranged for privacy, accessibility, and seamless workflow. In modern school building design, the admin block also acts as the central hub for communication, management, and school governance.
Below are the essential rooms and design considerations that every school’s administrative block must include for optimal efficiency and a professional campus environment.
- Reception & waiting area
- Principal office
- Vice-principal/HM office
- Admin office
- Accounts & record room
- Staff room
Expert Design Tips:
- Place the admin block near the main entrance
- Provide visitor control & security
- Ensure proper natural lighting
Laboratory Planning for Schools (CBSE Standards & Requirements)
Science laboratories are one of the most critical components of school building design, especially for middle and senior secondary levels. A well-planned school laboratory must comply with CBSE lab standards, ensure student safety, and provide an environment that supports hands-on learning, experimentation, and modern teaching methods.
Proper school lab requirements include adequate space, ventilation, chemical resistance, electrical safety, storage areas, and smooth circulation around workstations. Science labs such as Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Composite labs must meet specific size and infrastructure guidelines, while Computer Labs and Language Labs demand their own dedicated planning approach.
Designing a high-quality school laboratory is essential for CBSE affiliation, smooth inspections, and high-quality science education. Below are the essential laboratory types, size standards, infrastructure requirements, and safety guidelines every school must follow.
Essential Labs
- Physics
- Chemistry
- Biology
- Composite science lab
- Computer lab
- Language lab (optional)
Lab Design Requirements
- Minimum 600–800 sq ft
- Non-slippery flooring
- Ample ventilation
- Water & gas outlets, where required
- Storage & preparation room
School Library Planning (Design, Layout & Standards)
A well-designed school library is more than just a room with books — it is the intellectual centre of the campus. Modern school library design focuses on creating an inspiring, accessible, and technology-enabled learning environment where students can read, research, collaborate, and explore digital resources.
In school architecture, the library plays a key role in academic development, making it essential to plan the right size, layout, and functional zones based on school library requirements and CBSE recommendations. The space must support silent reading, digital learning, group activities, and efficient storage, while ensuring comfort, supervision, and ease of movement.
A well-planned library improves learning outcomes, encourages reading habits, and supports modern teaching methodologies through physical and digital resources.
Below are the essential components and design guidelines for planning an efficient library in a school.
- Reading hall
- Digital resource corner
- Book racks & storage
- Librarian’s desk
- Computer zone
Ideal size: 600–1,200 sq ft, depending on school size.
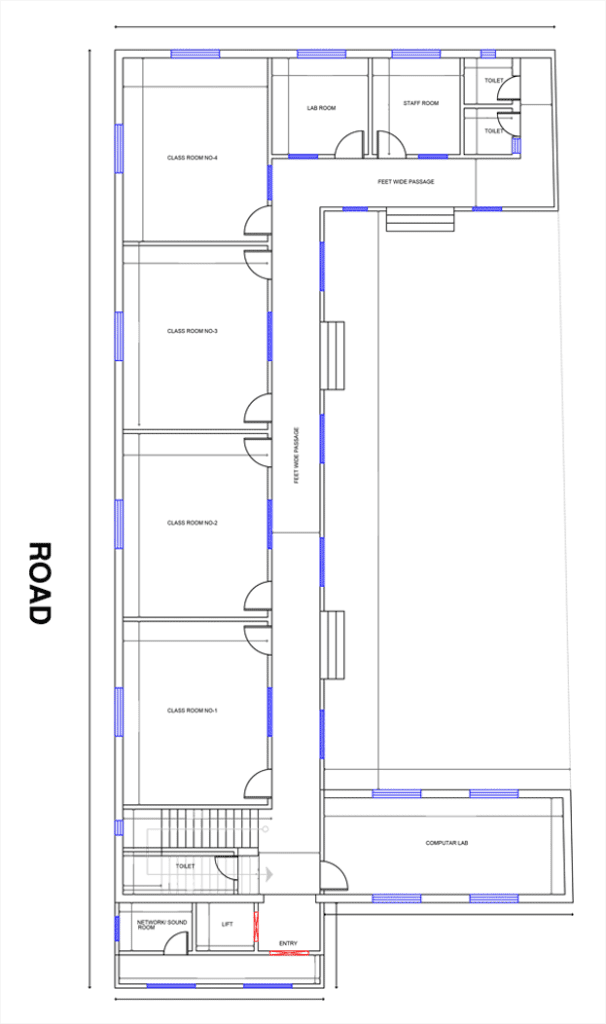

Circulation Planning in School Buildings (Corridors, Movement & Flow)
Efficient circulation is one of the most important — and often underestimated — aspects of school building design. Proper corridors, pathways, and movement zones ensure that students can transition between classrooms, labs, and activity areas safely and smoothly, without congestion or chaos. In India, modern campuses are increasingly designed around clear school building circulation standards to improve supervision, reduce bottlenecks, and enhance overall safety.
Well-planned circulation also supports emergency evacuation, prevents crowding during peak times, and improves visibility for teachers and staff. Corridor widths, staircase placement, entry/exit flow, and zoning transitions all play a crucial role in ensuring a safe and student-friendly movement pattern across the campus.
Below are the essential circulation guidelines and corridor design standards that every school should follow to achieve safe, efficient, and CBSE-compliant movement across all blocks.
- Corridor width: 6–10 ft
- Wider corridors near primary blocks
- Avoid bottlenecks & dead ends
- Ensure visibility for supervision
Staircase & Vertical Circulation Design in School Buildings
Staircases play a critical role in school building safety, circulation, and emergency movement. A well-planned school staircase design ensures that students can move between floors quickly, safely, and without congestion — especially during peak times such as morning arrival, recess, and dispersal. Proper vertical circulation planning is also essential for fire safety, evacuation routes, and compliance with the National Building Code (NBC) of India.
In multi-storey school buildings (G+1, G+2 or higher), staircase width, placement, railing height, slip resistance, and visibility become key architectural considerations. Schools must also plan for at least one fire escape staircase, adequate lighting, and clear signage to ensure smooth and safe movement across all levels.
Below are the essential staircase design standards and vertical circulation guidelines that every school should follow for a safe, compliant, and student-friendly campus.
- Minimum width: 1.5 m (5 ft)
- Fire staircase mandatory for G+2/G+3
- Railings at child-safe height
- Slip-resistant steps
Sanitary Facilities in Schools (Toilet Requirements & Hygiene Standards)
Proper sanitation is one of the most important components of school building design, directly impacting student health, comfort, attendance, and overall campus hygiene. In India, every school must comply with specific school toilet requirements set by CBSE, State Boards, and national hygiene guidelines to ensure safe and age-appropriate facilities for students and staff.
A well-planned school sanitation block must include adequate toilets for boys and girls, child-friendly fixtures for pre-primary sections, separate staff washrooms, accessible toilets for students with special needs, and properly ventilated handwashing areas. The design should support high footfall, quick cleaning, safe movement, and continuous water supply — all while maintaining strict hygiene standards.
Below are the essential toilet count norms, layout guidelines, and sanitation design standards every school in India must follow for compliance, comfort, and a healthy learning environment.
Toilet Count (General Guideline)
- 1 toilet per 25 girls
- 1 toilet + 1 urinal per 40 boys
- Separate staff toilets
- KG toilets must be inside classrooms
Design Tips
- Exhaust fans & natural ventilation
- Non-slippery floors
- Child-friendly fixtures for pre-primary
Playground & Outdoor Area Requirements for Schools
A well-designed playground is essential for a healthy and balanced school environment. As per modern school building planning standards, outdoor spaces contribute directly to a child’s physical development, social interaction, teamwork, motor skills, and emotional well-being. In India, both CBSE and State Boards emphasise the importance of adequate school playground size, sports fields, and open recreation areas for all age groups.
Playgrounds must be planned as safe, accessible, and multi-functional zones that support structured sports as well as free play. For pre-primary and primary students, activity spaces with soft flooring are essential, while middle and high school students require larger courts and fields suitable for organised sports. Proper fencing, shading, seating, drinking water points, and supervision areas are also key to safe outdoor activity.
Below are the essential outdoor area guidelines, sports field requirements, and playground planning standards every school should follow to create an engaging and student-friendly outdoor environment.
- Running area
- Sports courts
- Pre-primary play area
- Shaded zones
- Safe boundary wall
- Drinking water near the play area
Safety, Security & Compliance Standards for School Buildings
Safety is the foundation of every well-planned school campus. In India, strict school safety norms and compliance guidelines are mandated by CBSE, State Boards, the National Building Code (NBC), and local authorities to ensure that students, staff, and visitors remain protected at all times. These standards cover structural safety, fire protection, emergency exits, electrical installations, CCTV surveillance, and secure boundary design — all of which form the backbone of responsible school building planning.
A secure school must include well-lit corridors, safe staircases, fire-safety equipment, disaster management provisions, and controlled entry points. Modern school security requirements also emphasise visitor management, round-the-clock surveillance, and child-safe design, especially in pre-primary and primary blocks.
Ensuring proper safety and compliance not only protects the school community but is also essential for CBSE affiliation, long-term operations, and institutional reputation.
Below are the key safety guidelines, security measures, and compliance standards every school building must follow to remain safe, compliant, and future-ready.
- CCTV surveillance
- Boundary wall minimum 6 ft
- Fire extinguishers & hydrants
- Emergency exits
- Safe electrical installation
- Earthquake-resistant structure
MEP Requirements in School Buildings (Electrical, Plumbing & Ventilation)
MEP services (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing), form the core of a functional and safe school environment. Proper school MEP design ensures uninterrupted power, safe wiring, adequate lighting, clean water supply, efficient plumbing, and healthy ventilation across classrooms, labs, corridors, and outdoor areas. In India, these systems must comply with NBC guidelines, safety regulations, and school-specific operational needs.
Modern schools require reliable electrical load planning, child-safe switches, energy-efficient lighting, RO water points, proper drainage, exhaust ventilation in toilets, and fresh air movement in classrooms. Smart classrooms, computer labs, security systems, and CCTV surveillance also depend on robust electrical and network planning.
Below are the essential MEP standards every school building must follow to ensure safety, comfort, and long-term operational efficiency.
Electrical
- Adequate lighting
- Dedicated computer lab load
- Solar recommended
Plumbing
- Child-friendly sanitary fixtures
- RO water point
- Proper drainage
Ventilation / HVAC
- Cross-ventilated classrooms
- High ceilings
- Fresh air provisions
School Building Construction Cost in India (Quick Estimate for 2025)
Understanding the school building construction cost in India is essential for budgeting and project planning. While costs vary based on location, specifications, and facilities, most school projects fall within a predictable range. Here’s a quick snapshot of the estimated cost per sq ft and overall project budget for a standard CBSE school.
School Construction Cost in India (2025)
School construction cost in India in 2025 ranges from ₹1,600–₹2,800 per sq ft, depending on design, quality, and facilities. The cost varies from basic institutional construction to premium school infrastructure.
Cost Breakdown
- Structure & Civil Works: 55–60%
- MEP Services: 20–25%
- Finishing & Interiors: 15–25%
- Furniture & Fixtures: Separate additional cost
Use these numbers as a baseline; the actual cost of building your school will depend on design choices, amenities, and location-specific construction rates.
For detailed cost insights, you can also refer to our House Construction Cost Guide for India or use our Construction Cost Calculator to get a detailed construction cost breakup with BOM.
If you need an accurate, customised cost estimate for your school project, feel free to contact us. We’ll help you plan the entire project from concept to completion.
Over To You
A well-designed school is more than just a structure; it is an environment that shapes learning, safety, behaviour, creativity, and long-term student success. With thoughtful school building planning, compliance with CBSE norms, and architecture that prioritises ventilation, daylight, movement, and safety, you can create a campus that remains functional, inspiring, and future-ready for decades.
If you’re planning to build a school in India and need expert guidance, our team at Houseyog can help you with:
- Complete school master planning
- Architectural floor plans and design
- 3D elevation and exterior concept development
- MEP planning (Electrical, Plumbing, HVAC)
- CBSE compliance guidance and documentation
Call/WhatsApp Houseyog: +91 75960 58808
For professional assistance in designing your school project—aligned with safety norms, CBSE requirements, and modern educational needs, contact us anytime..
FAQs
The minimum land required to build a school in India is 1 acre for urban areas and 1.5–2 acres for rural areas, as per CBSE affiliation norms. Some State Boards may allow smaller plots for primary schools.
The ideal classroom size for 35–40 students is 540–600 sq ft, with dimensions around 28 × 20 ft. The minimum acceptable size is 430–480 sq ft.
A CBSE school must include:
Adequate classrooms
Science labs
Library
Admin block
Staff rooms
Playground
Safe drinking water
Separate toilets for boys and girls
Fire safety systems
CCTV and boundary wall
These form the core CBSE infrastructure requirements.
Building a school in India typically costs ₹1,600–₹2,800 per sq ft, depending on materials, design, and facilities. A 1-acre CBSE school generally costs 4.5 crore to ₹12 crore.
A CBSE secondary school must have:
Physics lab
Chemistry lab
Biology lab
Composite science lab
Computer lab
Senior secondary schools require additional specialised labs based on the subjects offered.
A school master plan should cover:
Academic blocks
Admin block
Playground and sports areas
Traffic circulation
Parking & service zones
Toilets and sanitation
Labs, library, and activity rooms
Future expansion areas
School corridors should be 6–10 ft wide, with primary blocks requiring wider corridors for safe student movement.
Key school safety norms include:
Fire extinguishers and hydrants
Emergency exits
Non-slippery floors
Boundary wall: minimum 6 ft
CCTV surveillance
Safe electrical wiring
Earthquake-resistant structure
Yes. CBSE strongly prefers schools with a proper playground. Ideal playground size is 12,000–15,000 sq ft, depending on total plot area.
A school library should be 600–1,200 sq ft, depending on the student population, and must include reading spaces, digital resources, and librarian supervision zones.
General guidelines:
1 toilet per 25 girls
1 toilet + 1 urinal per 40 boys
Separate staff toilets
Attached toilets for KG/pre-primary
These follow standard school sanitation guidelines
The best shape for a classroom is rectangular, with an aspect ratio of 1:1.3 to 1:1.4. Square rooms reduce visibility and seating efficiency.
Schools typically need:
Building plan approval
Fire safety NOC
Stability certificate
Sanitation certificate
Electrical safety approval
CBSE/State Board affiliation requirements
For primary schools, some states allow smaller plot sizes (e.g., 2,000–10,000 sq ft), but full CBSE secondary/senior secondary schools almost always require 1 acre or more.
To get CBSE approval, schools must meet land requirements, building safety norms, lab and library standards, sanitation rules, and submit all documents during the affiliation process, including fire safety NOC, stability certificate, and building completion certificate.






